What is Wi-Fi 7?
1. Wi-Fi History
I believe people are already very familiar with the concept of Wi Fi. In fact, it is a wireless networking technology.
Previously, people connected to the internet through Ethernet cables, while Wi Fi was connected through wireless radio waves.
The most common is wireless routers, which convert wired network signals into wireless signals to achieve the goal of allowing terminal devices to connect to the internet.
 The development history of Wi-Fi can be traced back to the 1990s, when the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States lifted restrictions on the use of the 2.4GHz frequency band, enabling the rapid development of wireless local area network (WLAN) technology.
The development history of Wi-Fi can be traced back to the 1990s, when the Federal Communications Commission (FCC) in the United States lifted restrictions on the use of the 2.4GHz frequency band, enabling the rapid development of wireless local area network (WLAN) technology.
In 1997, the IEEE 802.11 standard was released, which provided technical support for the development of WLAN technology.
In 1999, the IEEE 802.11b standard was released, supporting higher data transfer rates up to 11Mbps.
In 2003, the IEEE 802.11g standard was released, with a maximum data transfer rate of 54Mbps, becoming the most mainstream Wi-Fi standard at that time.
In 2006, the IEEE 802.11n standard was released, now known as Wi-Fi 4, which supports higher data transfer rates and longer coverage, up to 600Mbps.
In 2013, the IEEE 802.11ac standard, also known as Wi-Fi 5, was released, which uses more efficient technology to support higher data transfer rates and larger network capacity, up to 6.9Gbps.
In 2019, the IEEE 802.11ax standard, also known as Wi-Fi 6, was released, which supports more devices to connect simultaneously and provides higher data transfer rates and better network performance, up to 9.6Gbps.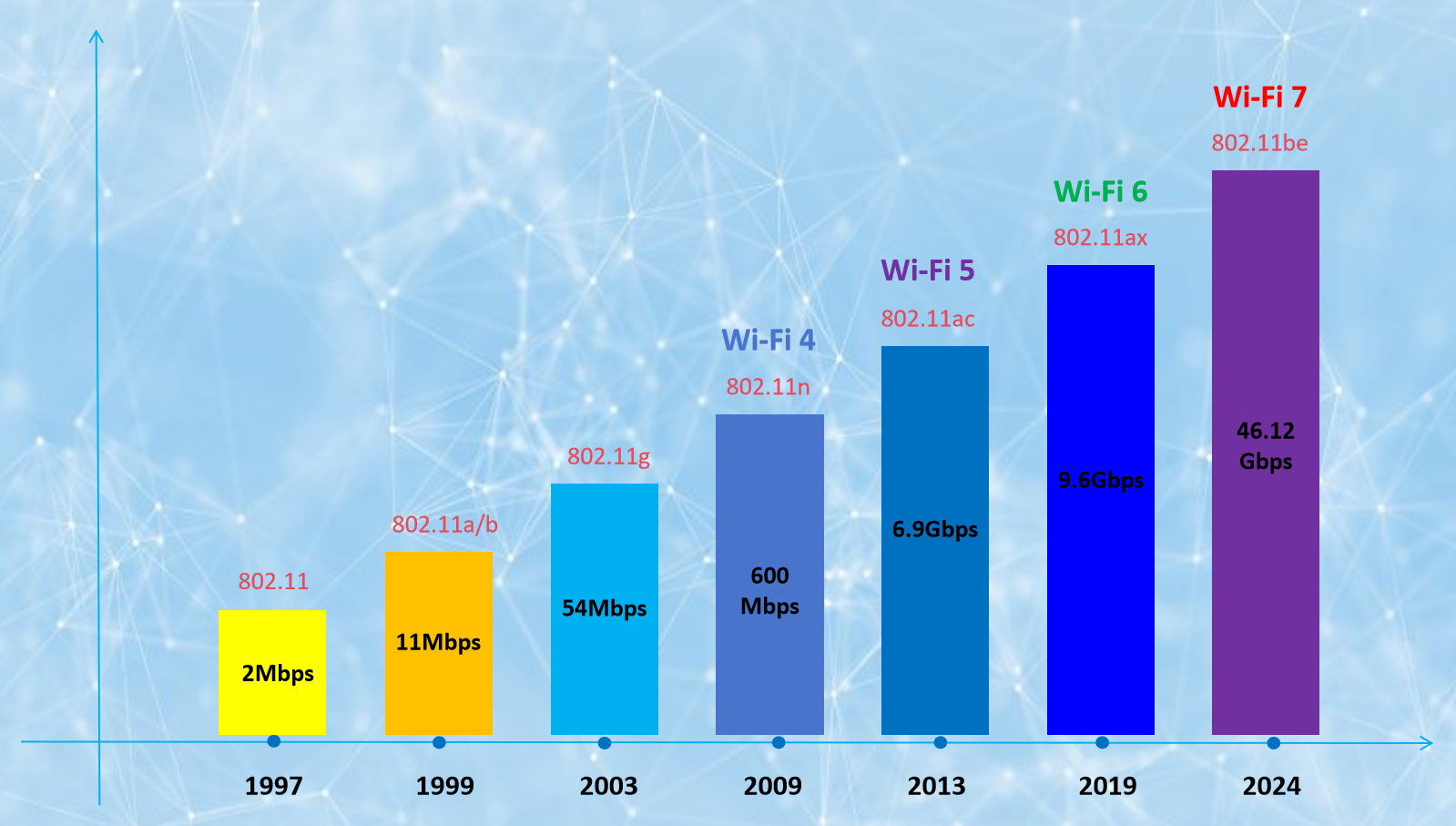 2. What is Wi-Fi 7?
2. What is Wi-Fi 7?
The Wi-Fi Alliance will release the IEEE 802.11be standard in 2024, which is now known as the seventh generation wireless network technology Wi-Fi 7.
 3. Wi-Fi 7 Technology Advantages
(1) Extremely High Transmission Rate
3. Wi-Fi 7 Technology Advantages
(1) Extremely High Transmission Rate
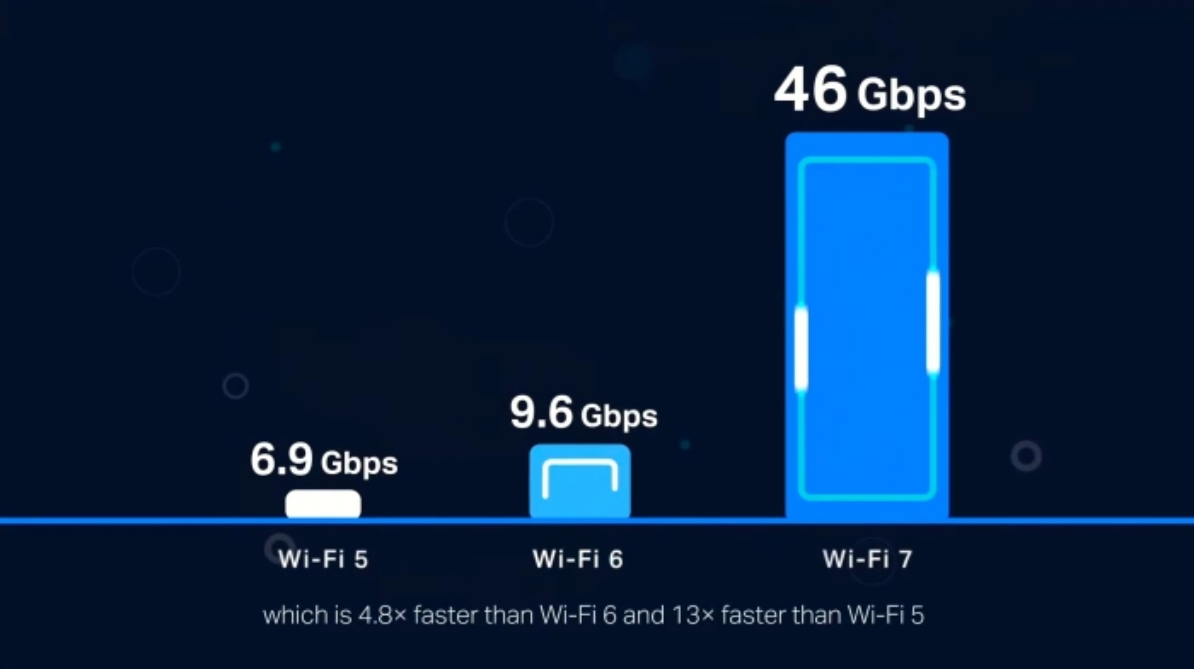
Compared to Wi-Fi 6, Wi-Fi 7 can reach a maximum speed of 46G, which is approximately 5 times that of Wi-Fi 6 (9.6GHz). This provides a solid foundation for advanced applications such as the Internet of Things and 8K videos in the future.
 (2) More spatial flow
(2) More spatial flow
Firstly, Wi-Fi 7 supports more spatial streams and introduces CMU-MIMO. Wi-Fi 6 supports up to 8 spatial streams, and the introduction of MU-MIMO is a major upgrade, allowing multiple devices to communicate with access points using multiple spatial streams simultaneously. Wi-Fi 7 devices can support 16 spatial streams, which is twice the size of Wi Fi 6. Supporting more data streams will also bring more powerful features such as CMU-MIMO. Among them, “C” represents Coordinated, which means that 16 data streams can be provided simultaneously by multiple access points instead of one.
CMU-MIMO is a new feature that caters to the development direction of multiple access points in wireless networks. To expand the coverage of Wi-Fi networks, Mesh networking is often used, which actually increases the number of access points; CMU-MIMO allows users to fully utilize the additional access points, diverting 16 data streams to different access points while working simultaneously.
 (3) New 6GHz frequency band and triple band collaborative operation
(3) New 6GHz frequency band and triple band collaborative operation
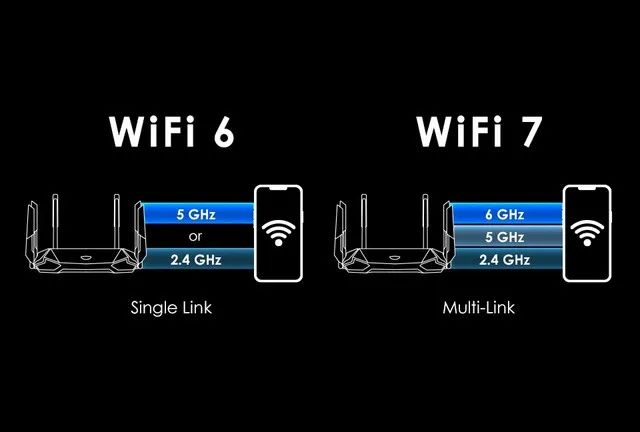
Secondly, Wi-Fi 7 also introduces a new 6GHz frequency band, with all three frequency bands operating simultaneously. As is well known, Wi-Fi 6 can use both 2.4GHz and 5GHz frequency bands simultaneously, and its upgraded version, Wi-Fi 6E, introduces a new 6GHz frequency band. Wi-Fi 7 will continue to use this new 6GHz frequency band.
In addition, Wi-Fi 7 also introduces Multi-Link Operation (MLO) technology, which includes multiple RF chips, 2.4GHz chips, 5GHz chips, and 6GHz chips in one AP. Multiple chips of AP can establish link communication with a single STA simultaneously. MLO is a MAC layer technology that can bundle multiple links across frequency bands into a virtual link.
Multi link transmission technology caters to the new characteristics of wireless network multi access point development direction, allowing users to fully utilize the extra access points and strive to achieve the goal of using three frequency bands for communication simultaneously, thereby obtaining larger communication bandwidth to increase their own speed, and also expanding the width of a single channel, doubling from 160MHz in Wi Fi 6 to 320MHz.
 (4) Larger data capacity
(4) Larger data capacity
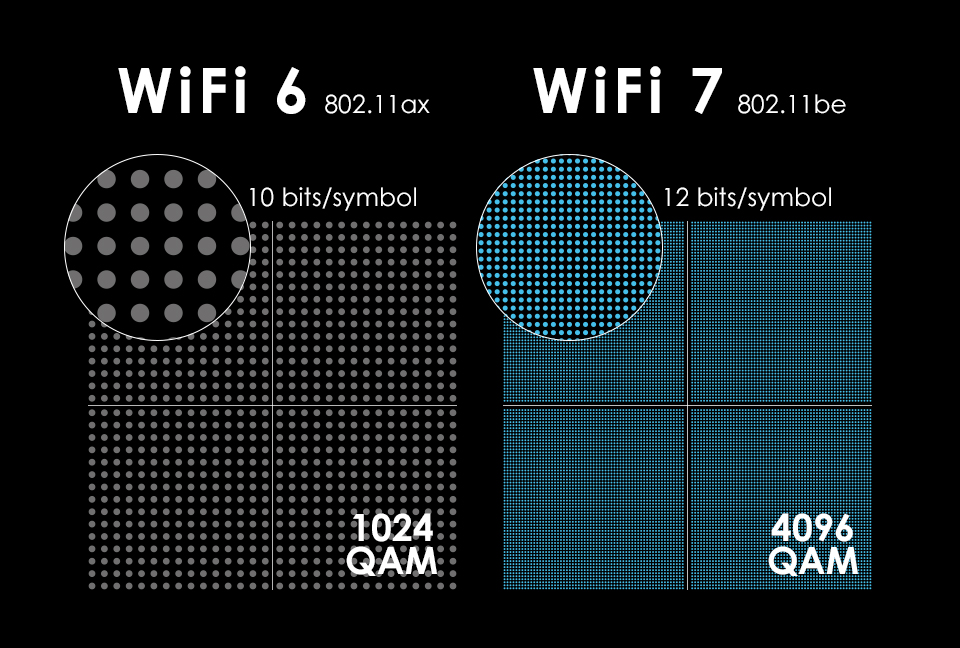
Wi-Fi 7 has upgraded the signal modulation method to 4096QAM for greater data capacity. Wireless technology will certainly involve signal modulation methods. In 802.11ax, the standard is 1024-QAM modulation, while Wi-Fi 7 is expected to continue upgrading the modulation methods and directly use 4096-QAM to further expand the transmission data capacity and lay the foundation for the highest 46Gbps.
 4. Disadvantages of Wi-Fi 7
(1) Time is far away
4. Disadvantages of Wi-Fi 7
(1) Time is far away
Wi-Fi will release the IEEE 802.11be (Wi-Fi 7) standard in 2024, and it will take several more years to promote and popularize it, especially with hardware updates for terminal devices.
(2) Expensive prices
Leaving aside Wi-Fi 7, the current price of Wi-Fi 6 is not yet as satisfactory, let alone the price of Wi-Fi 7. To popularize Wi-Fi 7, the first step is to lower the price in order to better meet market demand.



 2. What is Wi-Fi 7?
2. What is Wi-Fi 7?




